Guidelines for the correct use of granular NPK compound fertilizer: Doubling fertilizer efficiency and minimizing waste
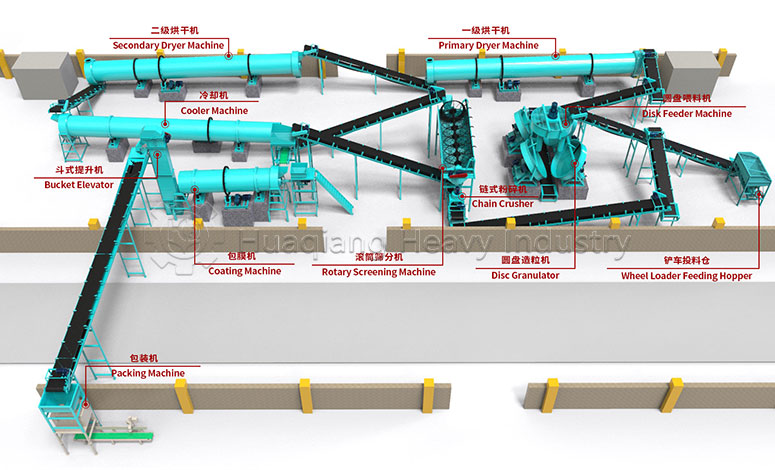
Granular NPK compound fertilizers are widely used in various crop cultivation due to their advantages of convenient storage, suitability for mechanized application, and stable nutrient release. This is thanks to the granulation technology of granular NPK compound fertilizers, which are processed and shaped by professional fertilizer granulators, ensuring both granule strength and nutrient stability.
Precise fertilizer selection and dosage control are prerequisites. Select the appropriate ratio based on soil testing and crop type; leafy vegetables require a high-nitrogen formula, while fruit trees during the fruit expansion stage require a high-potassium formula. Apply 20-40 kg per mu for field crops, and increase the amount appropriately for fruits and vegetables, avoiding excessive application to prevent soil compaction.
Flexible application methods are crucial. For fruit trees and vegetables, furrow application or hole application is suitable, applying the fertilizer 10-15 cm away from the roots and covering with soil to prevent root burn; for field crops, simultaneous sowing of fertilizer and seeds is possible, with a distance of ≥5 cm between the granular fertilizer and seeds; for seedlings or topdressing, broadcasting is suitable, combined with irrigation to promote absorption, and is compatible with mechanized operations.
Control the timing and combination of application. Apply base fertilizer 1-2 weeks before sowing/transplanting, and apply topdressing during the peak nutrient demand period of the crop. Combine with organic fertilizers and trace element fertilizers to enhance fertilizer efficiency, avoiding long-term single application leading to imbalance; customized granular fertilizers produced through standardized granulation technology on an NPK fertilizer production line offer even better results.
Pay attention to storage and application precautions. Store in a well-ventilated and dry place to prevent caking, and avoid mixing with acidic fertilizers; water promptly after application to promote dissolution, avoid excessive watering, and reduce nutrient leaching to maximize fertilizer efficiency.