NPK fertilizer production line: Targeting precise nutrients from diverse materials
NPK fertilizers can be formulated with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients according to crop needs, becoming “customized” fertilization solutions for agriculture. The core capability of this NPK fertilizer production line lies in its flexible handling of diverse materials.
First and foremost is the “difference” in the form of raw materials. The nitrogen source for NPK may be granular urea or powdered ammonium chloride, the phosphorus source is often lumpy monoammonium phosphate, and the potassium source is mostly free-flowing potassium chloride granules. The production line must first use crushing and grinding processes to grind the lumpy phosphorus source into fine powder, and then adjust the different forms of nitrogen and potassium raw materials into a homogeneous intermediate to avoid “particle clumping and powder settling” during subsequent mixing, ensuring that each nutrient is evenly distributed.
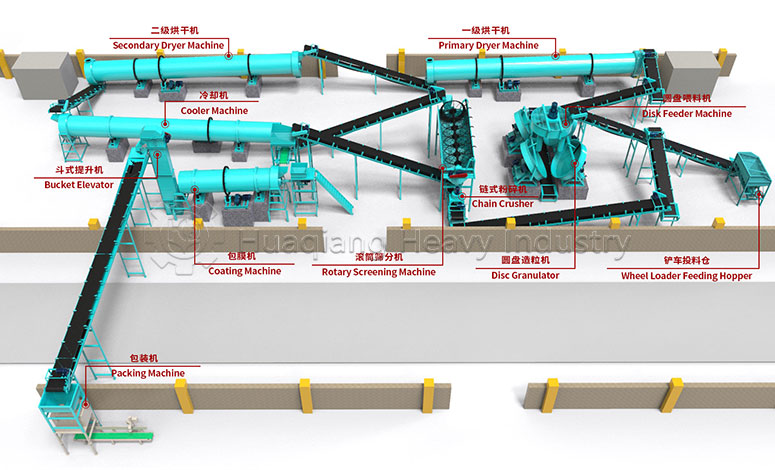
Secondly, there are the “special” physical and chemical properties of the materials. Some nitrogen sources tend to clump after absorbing moisture; for example, urea will harden into lumps when damp. Phosphorus sources have lower corrosivity, while potassium sources need to be protected from high temperatures to prevent nutrient loss. This requires the NPK fertilizer production line to “prescribe the right medicine for the right disease” during processing.
Finally, there is the “flexibility” of the material ratio. Different crops require different NPK ratios; for example, rice needs high nitrogen and low potassium, while fruits and vegetables need high potassium and low phosphorus. The production line needs to use a precise metering system to adjust the input of each raw material according to the formula at any time during material processing. In short, the NPK fertilizer production line“Strength” lies in the meticulous handling of diverse materials.
